Brute-force attack
Содержание:
- Theoretical limits[edit]
- Двухэтапная авторизация
- Дополнительные инструменты
- An introduction to brute force attacks
- Brute Force Attack Prevention with Imperva
- Preparing Web Security Dojo
- Blocking Brute Force Attacks
- Утёкшие пароли
- Ликбез
- Брутфорс: как пользоваться
- По другую сторону баррикады
- Brute-force attack
- How can it happen?
- Using Python to Brute Force DVWA (High Security)
- 11. Отключение вывода ошибок авторизации
Theoretical limits[edit]
The resources required for a brute-force attack grow exponentially with increasing key size, not linearly. Although U.S. export regulations historically restricted key lengths to 56-bit symmetric keys (e.g. Data Encryption Standard), these restrictions are no longer in place, so modern symmetric algorithms typically use computationally stronger 128- to 256-bit keys.
There is a physical argument that a 128-bit symmetric key is computationally secure against brute-force attack. The so-called Landauer limit implied by the laws of physics sets a lower limit on the energy required to perform a computation of kT · ln 2 per bit erased in a computation, where T is the temperature of the computing device in kelvins, k is the Boltzmann constant, and the natural logarithm of 2 is about 0.693. No irreversible computing device can use less energy than this, even in principle. Thus, in order to simply flip through the possible values for a 128-bit symmetric key (ignoring doing the actual computing to check it) would, theoretically, require 2128 − 1 bit flips on a conventional processor. If it is assumed that the calculation occurs near room temperature (~300 K), the Von Neumann-Landauer Limit can be applied to estimate the energy required as ~1018joules, which is equivalent to consuming 30 of power for one year. This is equal to 30×109 W×365×24×3600 s = 9.46×1017 J or 262.7 TWh (about 0.1% of the yearly world energy production). The full actual computation – checking each key to see if a solution has been found – would consume many times this amount. Furthermore, this is simply the energy requirement for cycling through the key space; the actual time it takes to flip each bit is not considered, which is certainly greater than 0.
However, this argument assumes that the register values are changed using conventional set and clear operations which inevitably generate entropy. It has been shown that computational hardware can be designed not to encounter this theoretical obstruction (see reversible computing), though no such computers are known to have been constructed.[citation needed]
Modern GPUs are well-suited to the repetitive tasks associated with hardware-based password cracking
A single COPACOBANA board boasting 6 Xilinx Spartans – a cluster is made up of 20 of these
AES permits the use of 256-bit keys. Breaking a symmetric 256-bit key by brute force requires 2128 times more computational power than a 128-bit key. One of the fastest supercomputers in 2019 has a speed of 100 petaFLOPS which could theoretically check 100 million million (1014) AES keys per second (assuming 1000 operations per check), but would still require 3.67×1055 years to exhaust the 256-bit key space.
An underlying assumption of a brute-force attack is that the complete keyspace was used to generate keys, something that relies on an effective random number generator, and that there are no defects in the algorithm or its implementation. For example, a number of systems that were originally thought to be impossible to crack by brute force have nevertheless been cracked because the key space to search through was found to be much smaller than originally thought, because of a lack of entropy in their pseudorandom number generators. These include Netscape’s implementation of SSL (famously cracked by Ian Goldberg and David Wagner in 1995}}) and a Debian/Ubuntu edition of OpenSSL discovered in 2008 to be flawed. A similar lack of implemented entropy led to the breaking of Enigma’s code.
Двухэтапная авторизация
Защита файлов и директорий паролем в cPanel
Можно установить защиту паролем на любую директорию на сервере средствами встроенного модуля веб-сервера. Для хостинга на базе панели cPanel нужно нажать в панели Файлы — Конфиденциальность каталога.

На следующем экране выберите папку, которую вы хотите защитить (/home/username/public_html/wp-admin). При нажатии на иконку слева происходит открытие каталога, при нажатие на название каталога — выбор.
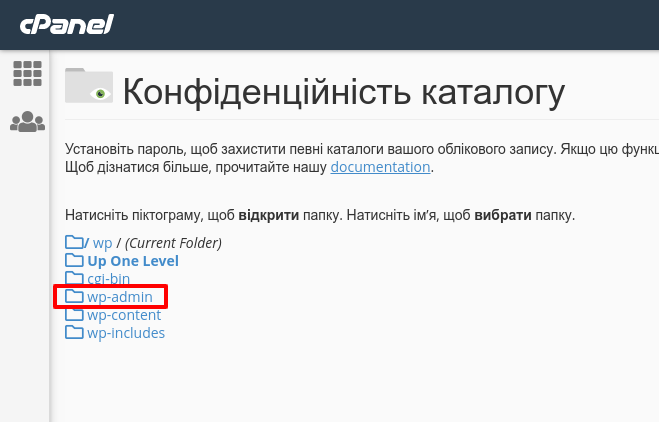
Далее укажите логин и пароль и включите защиту. Вы же помните, что пароли должны отвечать критериям из пункта 1? Ну и, конечно, не устанавливайте одинаковые пароли на различные формы ввода.

В результате этих действий в папке wp-admin будет создан файл .htaccess с такими настройками:
AuthType Basic AuthName "Autorize" AuthUserFile "/home/username/.htpasswds/domain.com/passwd" require valid-user
К сожалению, интерфейс панели управления не предусматривает защиту файла wp-login.php. Потому нужно скопировать фрагмент выше и вставить его в основной файл .htaccess в папке вашего сайта (обычно это /home/username/public_html) таким образом:
<FilesMatch "wp-login.php"> AuthType Basic AuthName "Autorize" AuthUserFile "/home/username/.htpasswds/domain.com/passwd" require valid-user </FilesMatch>
Защита файлов и директорий паролем в Apache
Если у вас панель управления не cPanel, или вообще нет панели управления на сервере, то можно просто добавить такие строки, как указано выше. После чего нужно сгенерировать сам файл доступа (прописан в строке AuthUserFile). Пароли в данный файл записываются в зашифрованном виде. Для шифрования пароля можно использовать сервис (тип кодировки нужно указать MD5). Полученные строчки нужно вписать в файл паролей, который в примере записан как /home/username/.htpasswds/domain.com/passwd
Содержимое файла passwd должно выглядеть примерно так:
admin:$apr1$jO5DLVTA$/KiKawt4F52ZNnTISPC1y/ editor:$apr1$BsN/.Ddj$zSgP0RrJpvgazIS4D23Ce/
Защита файлов и директорий паролем в Nginx
И в случае использования только веб-сервера Nginx — добавьте такие строчки в файл конфигурации для сайта (в блоке server):
location ~* ^/(wp-admin|wp-login.php)
{
auth_basic "Unauthorized";
auth_basic_user_file "/home/username/.htpasswds/domain.com/passwd";
}
Если хотите комбинировать эту настройку с ограничением доступа из пункта 3 данной статьи, то достаточно добавить только две строки, описывающие авторизацию внутрь блока, ограниченного фигурными скобками. Если вы продублируете блок location ниже, то в результате будет получена ошибка при перезапуске веб-сервера Nginx.
Для проверки правильности конфигурационного файла Nginx и перезагрузки веб-сервера в командной строке нужно выполнить:
~# nginx -t ~# systemctl restart nginx
Путь к файлу, который выше указан как «/home/username/.htpasswds/domain.com/passwd» может быть любой. Главное, чтобы пользователь, от имени которого работает Nginx, имел права на его чтение. Содержимое данного файла формируется точно так же, как и при настройке для веб-сервера Apache.
Дополнительные инструменты
Программы для брута хешей — это лишь малая часть софта из арсенала хешкрекера. Вернее, это его самая простая часть — взял файл с хешами, настроил нужные атаки и запустил. Всё — программа может крутиться сутками. Только поглядывай, сколько процентов хешей сломано.
Обычно через хешкрекера проходит множество всевозможных текстовых файлов:
- списки хешей в разных видах и форматах, часто с перемешанными хешами разных типов, и нужно извлечь хеши отдельно по каждому алгоритму;
- словари, которые надо чистить, сортировать, удалять повторы;
- накопленные результаты брута, в которых часто перемешаны и несоленые хеши с паролями, и соленые хеши с паролями,
и так далее.
В общем, сотни и тысячи подобных разнородных файлов — это еще та головная боль. И все выкручиваются по-разному — кто-то в том же линуксе делает часть работы командами самой ОС (например, grep), кто-то пишет себе скрипты на Perl, кто-то использует различные программы. Но факт очевиден — помимо брутфорсеров, нужны еще инструменты, которые должны работать с текстовыми файлами: сортировать, чистить, конвертировать из одного формата в другой, извлекать или переставлять данные, проверять формат и так далее.
Без этих инструментов работать крайне сложно, и поэтому с каждым брутфорсером обычно поставляется свой комплект различных утилит. И hashcat имеет такой комплект, и JtR тоже, но самый крупный комплект утилит под Windows имеет программа Hash Manager. В ней более 70 инструментов, построенных по принципу одна функция = один файл. Таким образом, из них, как из кирпичиков, можно собрать BAT-файл, выполняющий обработку файлов любой сложности. А 64-битные версии инструментов позволяют обрабатывать файлы неограниченного размера.
Вот пример BAT-файла, демонстрирующий, как из списка, в котором перемешаны хеши разных типов, вытащить только хеши от Magento с двухсимвольной солью:
REM Извлекаем только строки длиной 35 символов ExtractLinesByLen.exe %1 35 35 REM Переименовываем файл с извлеченными строками в файл 2.txt MOVE /Y %1.Lines 2.txt REM Проверяем формат хешей IsCharset.exe 2.txt ?h 1 REM Проверяем формат соли IsCharsetInPos.exe 2.txt 33 ':' IsCharsetInPos.exe 2.txt 34 ?l?u?d IsCharsetInPos.exe 2.txt 35 ?l?u?d REM Готово! В файле 2.txt остались только хеши от Magento
В дистрибутиве программы Hash Manager, в папке , можно найти около 30 готовых примеров, выполняющих различные полезные функции для хешкрекера.
An introduction to brute force attacks
Brute force attacks are often referred to as brute force cracking. Indeed, brute force — in this case computational power — is used to try to crack a code. Rather than using a complex algorithm, a brute force attack uses a script or bot to submit guesses until it hits on a combination that works.
There are easily available to help hackers launch brute force attempts. But even writing a script from scratch wouldn’t be too much of a stretch for someone comfortable with code. While these attacks are easy to execute, depending on the length and nature of the password and the computational power used, they could take days, weeks, or even years to be successful.
It’s worth noting that brute force attacks are re-entering the spotlight in 2020 as cybercriminals take advantage of the increase in the number of remote workers. An April 2020 report from Kaspersky found that the number of brute force attacks on Remote Desktop Protocols (RDPs) increased 400 percent in March and April.
 Source: Kaspersky
Source: Kaspersky
Before we look at how to spot and prevent brute force attacks, we should note some other terms you may come across related to this topic.
Hybrid brute force attacks
A brute force attack uses a systematic approach to guessing that doesn’t use outside logic. Similar attacks include a dictionary attack, which might use a list of words from the dictionary to crack the code. Other attacks may start with commonly used passwords.
These are sometimes described as brute force attacks. However, because they use some logic to decide which iterations may be the most likely first, they are more accurately referred to as hybrid brute force attacks.
Reverse brute force attack
A reverse brute force attack involves using a common password or group of passwords against multiple possible usernames. This doesn’t target a single user but might be used to try to gain access to a particular network.
The best protection against this type of attack is to use strong passwords, or from an administrator’s point of view, require that strong passwords are used.
Credential stuffing
Credential stuffing is a unique form of brute force attack that uses breached username and password pairs. If a username/password pairing is known, an attacker can use it to attempt to gain access to multiple sites. Once in a user’s account, they have full control over that account and access to any of the details it holds.
Precautions like two-factor authentication and security questions can help prevent damage by these kinds of attacks. However, the best protection is for users to never use the same password for multiple accounts.
Brute Force Attack Prevention with Imperva
Imperva Bot Protection monitors traffic to your website, separating bot traffic from real users and blocking unwanted bots. Because almost all brute force attacks are carried out by bots, this goes a long way towards mitigating the phenomenon.
Bot Protection follows three stages to identify bad bots. It classifies traffic using a signature database with millions of known bot variants. When identifying a suspected bot, it performs several types of inspection to classify the bot as legitimate, malicious or suspicious. Finally, suspicious bots are challenged, to see if they can accept cookies and parse Javascript.
Preparing Web Security Dojo
Install the programs we need and update a little (this is inside Web Security Dojo):
sudo apt update # sudo apt dist-upgrade # if you wish, you can perform a complete system upgrade. If you did, then reboot after this step before continuing. sudo apt install python-pycurl curl sudo pip install --upgrade pip sudo pip install --upgrade pycurl
Download the latest version of the patator script:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lanjelot/patator/master/patator.py chmod +x patator.py ./patator.py
Also, note that I updated Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) and Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) to the latest versions. How to do this is described on the corresponding pages on the links given above.
We also need word lists (dictionaries). We download a couple, if they cannot find the password, then we will download more dictionaries:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/1N3/BruteX/master/wordlists/namelist.txt wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/1N3/BruteX/master/wordlists/password_medium.txt
The latest version of Burp Suite can be downloaded from: https://portswigger.net/DownloadUpdate.ashx?Product=Free
Blocking Brute Force Attacks
A common threat web developers face is a password-guessing attack known as a brute force attack.
A brute-force attack is an attempt to discover a password by systematically trying every possible combination of letters, numbers, and symbols until you discover the one correct combination that works.
If your web site requires user authentication, you are a good target for a brute-force attack.
An attacker can always discover a password through a brute-force attack, but the downside is that it could take years to find it.
Depending on the password’s length and complexity, there could be trillions of possible combinations.
To speed things up a bit, a brute-force attack could start with dictionary words or slightly modified dictionary words because most people will use those rather than a completely random password. These attacks are called dictionary attacks or hybrid brute-force attacks.
Brute-force attacks put user accounts at risk and flood your site with unnecessary traffic.
Hackers launch brute-force attacks using widely available tools that utilize wordlists and smart rulesets to intelligently and automatically guess user passwords. Although such attacks are easy to detect, they are not so easy to prevent.
For example, many HTTP brute-force tools can relay requests through a list of open proxy servers. Since each request appears to come from a different IP address, you cannot block these attacks simply by blocking the IP address.
To further complicate things, some tools try a different username and password on each attempt, so you cannot lock out a single account for failed password attempts.
Утёкшие пароли
Утёкшие или украденные с сайтов пароли. Из списков намеренно удалены имена / почтовые адреса и т.д.
Лучшее их применение – это генерация или тестирования списков словарей.
Примечание: Даты приблизительные.
| Имя | Название файла / ссылка на скачивание | Дата | Примечание |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rockyou | rockyou.txt.bz2 (60,498,886 bytes) | 2009-12 | Лучший из доступных списков; огромный, украдены в незашифрованном виде |
| Rockyou со счётчиком | rockyou-withcount.txt.bz2 (59,500,255 bytes) | ||
| phpbb | phpbb.txt.bz2 (868,606 bytes) | 2009-01 |
Отсортированы по частоте использования Взломаны Brandon Enright из md5 (покрытие 97%+) |
| phpbb со счётчиком | phpbb-withcount.txt.bz2 (872,867 bytes) | ||
| phpbb с md5 | phpbb-withmd5.txt.bz2 (4,117,887 bytes) | ||
| MySpace | myspace.txt.bz2 (175,970 bytes) | 2006-10 | Получены фишингом |
| MySpace — со счётчиком | myspace-withcount.txt.bz2 (179,929 bytes) | ||
| Hotmail | hotmail.txt.bz2 (47,195 bytes) | Неизвестно | Не до конца понятно, как они были украдены |
| Hotmail со счётчиком | hotmail-withcount.txt.bz2 (47,975 bytes) | ||
| Faithwriters | faithwriters.txt.bz2 (39,327 bytes) | 2009-03 | Религиозные пароли |
| Faithwriters — со счётчиком | faithwriters-withcount.txt.bz2 (40,233 bytes) | ||
| Elitehacker | elitehacker.txt.bz2 (3,690 bytes) | 2009-07 | Часть из zf05.txt |
| Elitehacker — со счётчиком | elitehacker-withcount.txt.bz2 (3,846 bytes) | ||
| Hak5 | hak5.txt.bz2 (16,490 bytes) | 2009-07 | Часть из zf05.txt |
| Hak5 — со счётчиком | hak5-withcount.txt.bz2 (16,947 bytes) | ||
| Älypää | alypaa.txt.bz2 (5,178 bytes) | 2010-03 | Финские пароли |
| alypaa — со счётчиком | alypaa-withcount.txt.bz2 (6,013 bytes) | ||
| Facebook (Pastebay) | (375 bytes) | 2010-04 |
Найдены на Pastebay; судя по всему, украдены зловредным ПО. |
| Facebook (Pastebay) — со счётчиком | (407 bytes) | ||
| Unknown porn site | porn-unknown.txt.bz2 (30,600 bytes) | 2010-08 | Найдены на angelfire.com. Неизвестно, откуда они, но определённо с порно сайта. |
| Unknown porn site — со счётчиком | porn-unknown-withcount.txt.bz2 (31,899 bytes) | ||
| Ultimate Strip Club List | tuscl.txt.bz2 (176,291 bytes) | 2010-09 | Спасибо Mark Baggett за находку! |
| Ultimate Strip Club List — со счётчиком | tuscl-withcount.txt.bz2 (182,441 bytes) | ||
| (14,457 bytes) | 2010-09 | Спасибо Andrew Orr за наводку | |
| Facebook Phished — со счётчиком | (14,941 bytes) | ||
| Carders.cc | carders.cc.txt.bz2 (8,936 bytes) | 2010-05 | |
| Carders.cc — со счётчиком | carders.cc-withcount.txt.bz2 (9,774 bytes) | ||
| Singles.org | singles.org.txt.bz2 (50,697 bytes) | 2010-10 | |
| Singles.org — со счётчиком | singles.org-withcount.txt.bz2 (52,884 bytes) | ||
| Unnamed financial site | (reserved) | 2010-12 | |
| Unnamed financial site — со счётчиком | (reserved) | ||
| Gawker | (reserved) | 2010-12 | |
| Gawker — со счётчиком | (reserved) | ||
| Free-Hack.com | (reserved) | 2010-12 | |
| Free-Hack.com со счётчиком | (reserved) | ||
| Carders.cc (second time hacked) | (reserved) | 2010-12 | |
| Carders.cc со счётчиком (second time hacked) | (reserved) |
Ликбез
Brute-force (атака полным перебором) – метод решения математических задач, сложность которого зависит от количества всех возможных решений. Сам же термин brute-force обычно используется в контексте хакерских атак, когда злоумышленник пытается подобрать логин/пароль к какой-либо учетной записи или сервису.
Рассмотрим инструменты, которые можно использовать для выполнения brute-force атак на SSH и WEB-сервисы, доступные в Kali Linux (Patator, Medusa, Hydra, Metasploit), а также BurpSuite и даже самый известный сетевой сканер nmap.
Brute-force SSH
Для примера возьмем тестовую машину 192.168.60.50 и попробуем подобрать пароль пользователя test по SSH.
Мы будем использовать популярные пароли из стандартного словаря rockyou.txt. Этот и другие словари доступны в свободном доступе на гитхабе.
Patator
Для подбора пароля средствами Patator используем команду:
где:ssh_login — необходимый модульhost – наша цельuser – логин пользователя, к которому подбирается пароль или файл с логинами для множественного подбораpassword – словарь с паролями-x ignore:mesg=’Authentication failed’ — команда не выводить на экран строку, имеющую данное сообщение. Параметр фильтрации подбирается индивидуально.
Hydra
Для подбора пароля используя Hydra выполним команду:
где:-V – показывать пару логин+пароль во время перебора-f – остановка как только будет найден пароль для указанного логина-P – путь до словаря с паролямиssh://192.168.60.50 – указание сервиса и IP-адрес жертвы
Medusa
Для подбора пароля с использованием Medusa выполним команду:
где:-h – IP-адрес жертвы-u – логин-P – путь к словарю-M – выбор модуля-f – остановка после нахождения валидной пары логин/пароль-v – настройка отображения сообщений на экране во время процесса подбора
Metasploit
Произведем поиск инструмента для проведения brute-force атаки по SSH:
search ssh_login и получили ответ:
Задействуем модуль:
Для просмотра необходимых параметров, воспользуемся командой show options. Для нас это:rhosts – IP-адрес жертвыrport – портusername – логин SSHuserpass_file – путь до словаряstop_on_success – остановка, как только найдется пара логин/парольthreads – количество потоков
Указание необходимых параметров производится через команду “set“.
Указав необходимые параметры набираем команду “run” и ждем.
Противодействие
Ограничить количество устанавливаемых соединений с использованием межсетевого экрана.
Пример настройки iptables:
Такое правило установит ограничение доступа к SSH для каждого IP-адреса до 1 соединения в секунду, значительно усложнив перебор. Также эффективным решением может быть использование двухфакторной аутентификации (например, используя eToken) или аутентификации с использованием ключевой пары, а также использование ACL на основе IP-адресов.
Брутфорс: как пользоваться
Далее рассмотрим, как пользоваться брутфорсом и для чего. Если говорить о легальных и благих намерениях, то он используется для проверки надёжности или восстановления паролей. Этим занимаются системные администраторы, используя при этом специализированные программы.
В ситуациях с иными намерениями существует три вида использования такого метода. Первый – это персональный взлом. Киберпреступник может как узнать номер электронного кошелька так и завладеть другими личными данными пользователей. Используя их в последствие, злоумышленник подбирает пароль получения доступа к его аккаунтам, электронной почте или сайту.
Второй вид брутфорса – брут-чек. В данном случае уже выступает цель завладения паролями именно в больших количествах, для последующей продажи аккаунтов и иных целей. И третьим видом является удалённый взлом компьютерной системы, с целью полного управления персональным компьютером жертвы. Зачастую, злоумышленники пишут программы для такого перебора самостоятельно, с использованием мощных компьютерных систем.
Если Вам была интересна данная статья, рекомендуем так же прочитать о разработке сайта-визитки под ключ и о том, как это происходит. Будьте внимательны и осторожны, распространяя свои личные данные, не подвергайте себя риску и не занимайтесь преступной деятельностью.
По другую сторону баррикады
Теперь посмотрим на хеши глазами администратора того ресурса, который он хочет максимально защитить от взлома. Как можно усложнить жизнь хешкрекеру или вообще сделать так, что хеши пользователей станут неломаемыми?
Иногда для этого достаточно перейти на самую свежую версию движка и выбрать алгоритм, самый медленный по скорости брута. Но если обновление движка не планируется, а администратор хочет максимально обезопасить пароли своих пользователей от подбора, то есть другой вариант — пропатчить код проверки пароля так, чтобы у всех вновь зарегистрированных пользователей (или сменивших свои пароли после определенной даты) пароли хешировались по-другому. Как?
Конечно, можно использовать любой стандартный тяжелый алгоритм из Linux-функции crypt() — sha512crypt или bcrypt. Но если удастся заполучить такие хеши, то хешкрекер по сигнатурам сразу определит алгоритм и сможет ломать хеши (хоть и медленно). Вывод — нужно хешировать пароли так, чтобы хешкрекер не мог однозначно определить алгоритм по виду хеша, а это делается только нестандартными методами.
Например, можно подмешивать к паролю статическую соль (пусть даже одинаковую для всех, но очень длинную — 200–500 символов) и хешировать обычной PHP-функцией md5. Этой соли в БД форума нет (как, например, в движках vBulletin или osCommerce), она прошита только в PHP-коде, доступ к которому получить гораздо сложнее, чем к хешам. Но даже если заполучить эту соль, то почти нет брутфорсеров, поддерживающих работу с такой длинной солью (во всяком случае, на GPU — точно нет).
Другой вариант — циклически хешировать обычный MD5 от пароля этак 50–100 тысяч раз. На скорости авторизации пользователей это почти не скажется, но скорость брута таких хешей будет мизерной (при условии, что еще удастся выяснить количество итераций — опять же, только из PHP-кода). А если не удастся — то их вообще не сбрутить.
Еще можно взять более длинный хеш от другого алгоритма (например, SHA-256 или SHA-512) и вместо цельного хеша хранить в БД его фрагмент размером 32 символа из середины хеша (да еще и байты можно переставить). Хешкрекер, увидев такой хеш, будет уверен, что это MD5 (или его модификация), и будет пытаться сбрутить его, но бесполезно.
В общем, тут фантазия безгранична — автор за годы работы с хешами сталкивался с массой различных хитроумных видов хеширования, но факт налицо — очень много дампов от самописных CMS, или от коммерческих CMS без доступных исходников, или от пропатченных (по-видимому) форумов, и CMS остаются до сих пор несломанными. Что там внутри намешано при хешировании — неизвестно.
И нестареющий совет всем пользователям: самый надежный вариант защитить свой аккаунт от взлома, даже если был получен доступ к хешу от вашего пароля, — использовать длинный пароль, состоящий из случайных символов. Такие пароли не ломаются!
Brute-force attack
This definition was taken from the Wikipedia site. Well, to put it in simple words, brute-force attack guess a password by trying all probable variants by given character set. Eg. checking all combination in lower Latin character set, that is ‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz’. The brute-force attack is very slow. For example, once you set lower Latin charset for your brute-force attack, you’ll have to look through 217 180 147 158 variants for 1-8 symbol password. It must be used only if other attacks have failed to recover your password.
There are 3 group of options here:
Brute-force charset
Brute-force attack assumes using all possible variations from the specified character range, which is set in the first group of options. You can select and combine predefined character sets (e.g., Latin characters, numbers or special characters) or define your own ones. To define your own character set, select the option ‘Custom charset’. This will enable two fields for defining a custom character set: the first one — for entering ASCII or OEM characters, the second one — for entering non-printable characters. You can save your custom character set on disk. The program comes with several examples of user-defined character sets.Password length and position
The second group of options allows setting the minimum and maximum lengths of the password to be generated. If the last brute-force attack was interrupted or stopped, you can resume it from the last position saved by the program (see ‘Starting password’ option.)Distributed attack
This group of options can be useful when you have access to several computers. In this case, the entire set of characters to be verified, if it is too large, can be split into portions and attack the password by portions on several computers at the same time. To implement that, you will need to select the number of computers participating in the distributed attack (‘Number of computers to participate’ option), select the same settings for all computers, and assign each computer its number in the ‘Password range for computer’ drop-down list.
Below is a table that shows the time required to find 6 symbol password. Assuming that the brute-force speed is 1 million passwords per second.
| Charset file name | Charset string | Example | Total passwords | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-9.pcf | 0123456789 | 666929 | 1 111 110 | 1 sec |
| 1-13.pcf | 0x1 … 0xd | 5 229 042 | 5 sec | |
| a-z.pcf | abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz | qwerty | 321 272 406 | 5 min |
| a-z, 0-9.pcf | abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789 | asd123 | 2 238 976 116 | 37 min |
| a-z, 0-9, symbol14.pcf | abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789!@#$%^&*()-_+= | a#q1*9 | 15 943 877 550 | 4.5 hrs |
| a-z, A-Z.pcf | ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz | QWErty | 20 158 268 676 | 5,5 hrs |
| a-z, A-Z, 0-9.pcf | ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz 0123456789 | Asd123 | 57 731 386 986 | 16 hrs |
| a-z, A-Z, 0-9, symbol14.pcf | abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ 0123456789!@#$%^&*()-_+= | As12#$ | 195 269 260 956 | 2 days, 6 hrs |
| all.pcf | ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz 0123456789!\»#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@^_`{|}~»; | Aa1@|} | 742 912 017 120 | 8 days, 15 hrs |
How can it happen?
However, If You are interested in cracking passwords, you will have to use the computer.If you are a good coder then it will be easier to code the lines which can code the program easily.
Let’s suppose that you have developed a password that breaks the program which tries 1000 combinations per second but it takes around a minimum of 7 years.
Even if you want to do it faster!
You need a supercomputer. So, if we calculate the supercomputer then in just 22 seconds, all 218 trillion will be tested. But Can a Hacker purchase or create a supercomputer to perform this function?
Computing resources of this kind are not available for the common people. The password hackers are not common people who can collect the computing resources by different means for developing a powerful computing engine via software.
The calculation which are the possible combinations of an 8-character-password.but think if your password is the 10th combination or the 100th combinations. Why it is essential to have additional layers of the security in order to detect and deflect any password breaching attempt.
Hacker’s Motive Behind Every Act
The Brute Force attack which is done by the threat actor has some motive behind that even they try to gain illegal access to the target website and utilize it in either executing another kind of attack or stealing valuable data which simply used to break.
How Can I Prevent It?
You can take some precautionary measures :
- Password length
- Modifying .htaccess file
- Using captcha
- Two-factor Authentication.
- Cloudflare.
- Password Complexity.
- Limit login attempts.
Password length & Complexity :
The first step towards the Brute Force Attack prevention should be longer password length like “ I love* “ and “12345” instead of using these types of passwords to make sure to make it complex. The complexity of the password delays the cracking process.
Modifying .htaccess file
When you add a few rules in.htaccess file which further hardens to the security of your WordPress site. The objective is to allow the wp-admin which can only specific IP addresses listed in .htaccess file.
So open your .htaccess file and modify it like :
“
<Files /wp-login>
order deny, allow
allow from IP1
allow from IP2
deny from all
</Files>”
IP1 and IP2 will be the Ip that you allowed to access.Using Captcha :
If you are using captchas are most commonly used in websites. Even they prevent the boats from executing the automated scripts, mainly used in brute force attacks. The installing captcha in your WordPress site is fairly easy.
Two-factor Authentication :
The two-factor authentication is an extra line for the defense which can defend your account from the Brute Force attack. The chances of successfully executing the Brute Force Attack on the 2FA protected sites.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare is a renowned service for WordPress which usually deals with the CDN and caching.this company offers the protective shield against the Brute Force Attacks. Users can set rules for accessing the login pages and set Browser Integrity Check.
Limit the Login Attempts :
The powerful action is to limit the login attempts on WordPress which admin or another admin panel for that matter.
Found this article informative? Follow Vednam on , , Mix, Tumbler, and Linkedin to know more exclusive content we post.
You can Also read Articles :
Using Python to Brute Force DVWA (High Security)
While researching for this tutorial I come across a post over on medium by Danny Beton https://medium.com/@dannybeton/dvwa-brute-force-tutorial-high-security-456e6ed3ae39 where he covers step by step creating the python script that will allow you to capture the CSRF Token and brute force the login to DVWA on high security.
I did have to make a few changes to the original script from Danny’s page to get it working but only because I was having issues with the Password file adding 0x0n to the end of each brute force password attempt, I also wanted to see each password try output to the screen as the script runs.
Below is my edited version of Danny’s Python script which i saved as DVWA-BruteForce.py.
You will need to download the Python modules beautyfulsoup and requests for the script above to work as these are not part of the default pre installed modules in Python.
BeautyfulSoup is a web scrapping library used to capture the CSRF token. Requests are what he used to make the requests to the web server. He also used argv to supply arguments to the script from the command line but this module already comes installed.
These modules can be installed using pip with the commands below.
Also to get this to work you need to edit the URL = in the script to be the IP address of your DVWA web server, also you need to capture a PHPSESSID using Burp as we did previously in step 8 on the Low Security setting, add your PHPSESSID = to the script.
Run the Python Script using this command below adding the password list and the message which is received on a successful login.
If the Script works you should see an output like this..
11. Отключение вывода ошибок авторизации
Во время брут-форс атаки хакеру будет полезно видеть информацию о том, что введенные данные неверны. Сообщения об этом отображаются каждый раз при неудачной попытке входа, причем также сообщается, что именно — логин или пароль — неправильное. Поэтому возможно немного усложнить жизнь взломщикам: убрать эти уведомления.
Для этого достаточно добавить в functions.php темы вашего сайта всего одну строчку:
add_filter('login_errors',create_function('$a', "return null;"));
Редактировать файл можно любым удобным вам способом, как из админ-панели, так и по FTP или через файловый менеджер. Строчку нужно добавить в начале файла после открывающего тега (<?php ).
Это были самые на наш взгляд действенные методы защиты сайтов на WordPress от взломов методом брут-форс атаки. Вы можете выбирать какой-либо один или скомбинировать несколько. А в следующий раз мы познакомим вас с одним плагином, который объединяет в себе почти все описанные здесь методики защиты сайта.
Ежедневно сайты и плагины на тарифах WordPress хостинга от Hostpro проверяются на наличие уязвимостей. Каждую ночь мы делаем резервные копии вашего сайта и сохраняем их в течение месяца. В случае если ваш сайт будет взломан, мы восстановим его работу бесплатно. Перенесите свой сайт на Hostpro безопасно, быстро и совершенно бесплатно. Просто заполните заявку на нашем сайте.